Node graph
Node graphs can visualize directed graphs or networks. They use a directed force layout to effectively position the nodes, so they can display complex infrastructure maps, hierarchies, or execution diagrams.
image::node-graph-8-0.png
The following video provides beginner steps for creating node panel visualizations. You’ll learn the data requirements and caveats, special customizations, and much more:
Data requirements
A node graph requires a specific shape of the data to be able to display its nodes and edges. This means not every data source or query can be visualized with this graph. If you want to use this as a data source developer see the section about data API.
A node graph consists of nodes and edges.
-
A node is displayed as a circle. A node might represent an application, a service, or anything else that is relevant from an application perspective.
-
An edge is displayed as a line that connects two nodes. The connection might be a request, an execution, or some other relationship between the two nodes.
Both nodes and edges can have associated metadata or statistics. The data source defines what information and values is shown, so different data sources can show different type of values or not show some values.
Nodes
NOTE: Node graphs can show only 1,500 nodes. If this limit is crossed a warning will be visible in upper right corner, and some nodes will be hidden. You can expand hidden parts of the graph by clicking on the “Hidden nodes” markers in the graph.
Usually, nodes show two statistical values inside the node and two identifiers just below the node, usually name and type. Nodes can also show another set of values as a color circle around the node, with sections of different color represents different values that should add up to 1.
For example, you can have the percentage of errors represented by a red portion of the circle. Additional details can be displayed in a context menu which is displayed when you click on the node. There also can be additional links in the context menu that can target either other parts of Grafana or any external link.
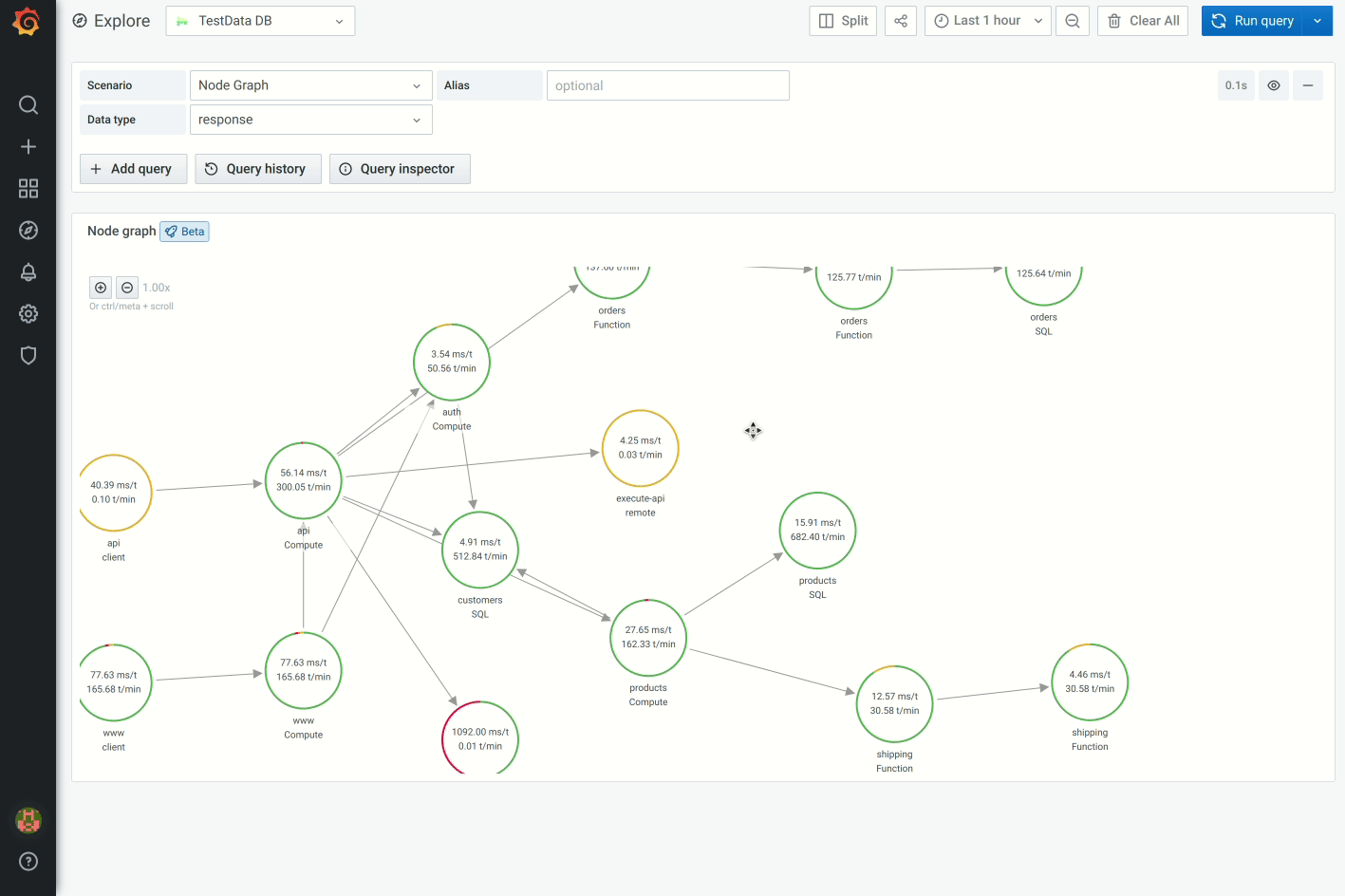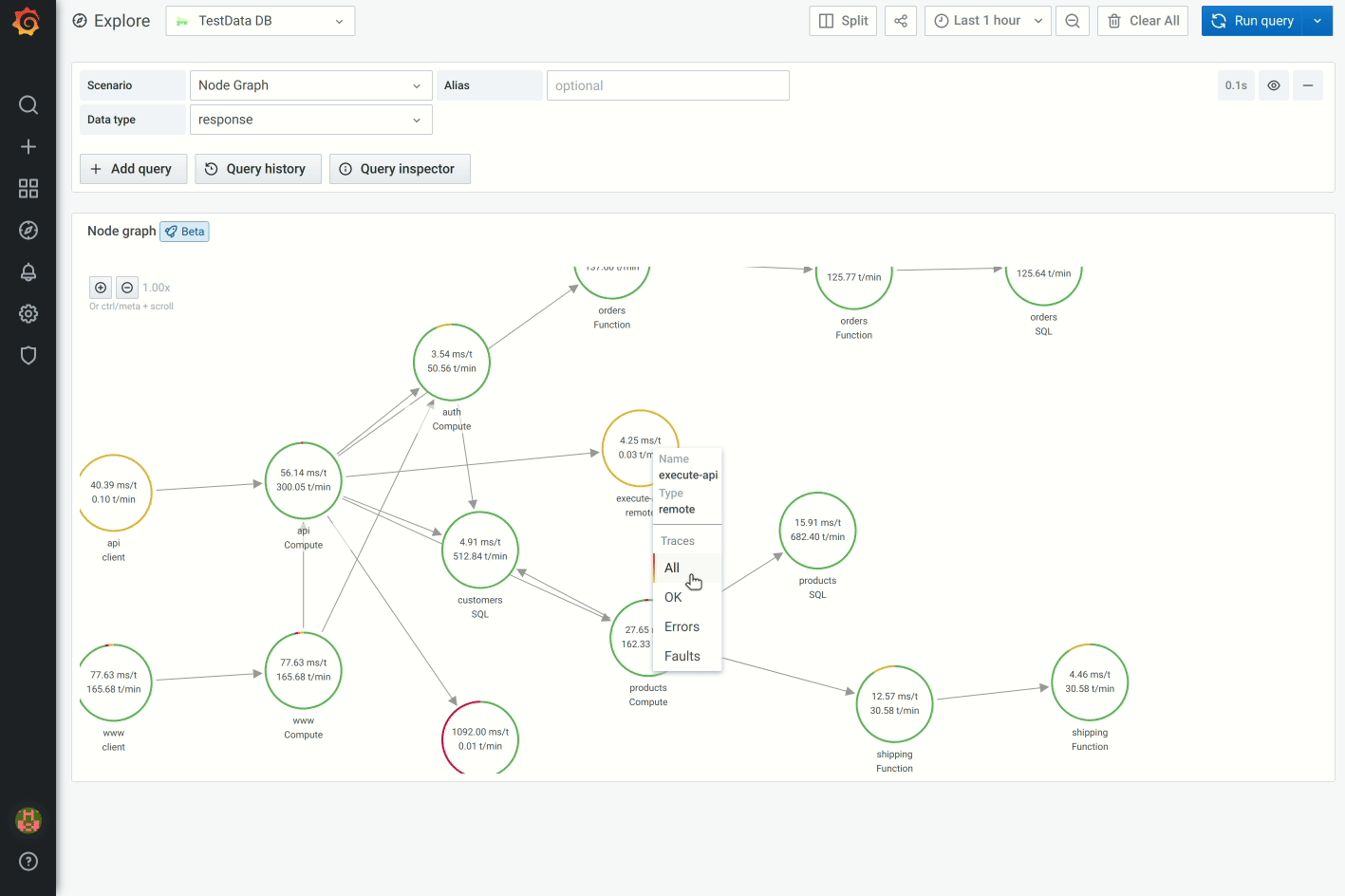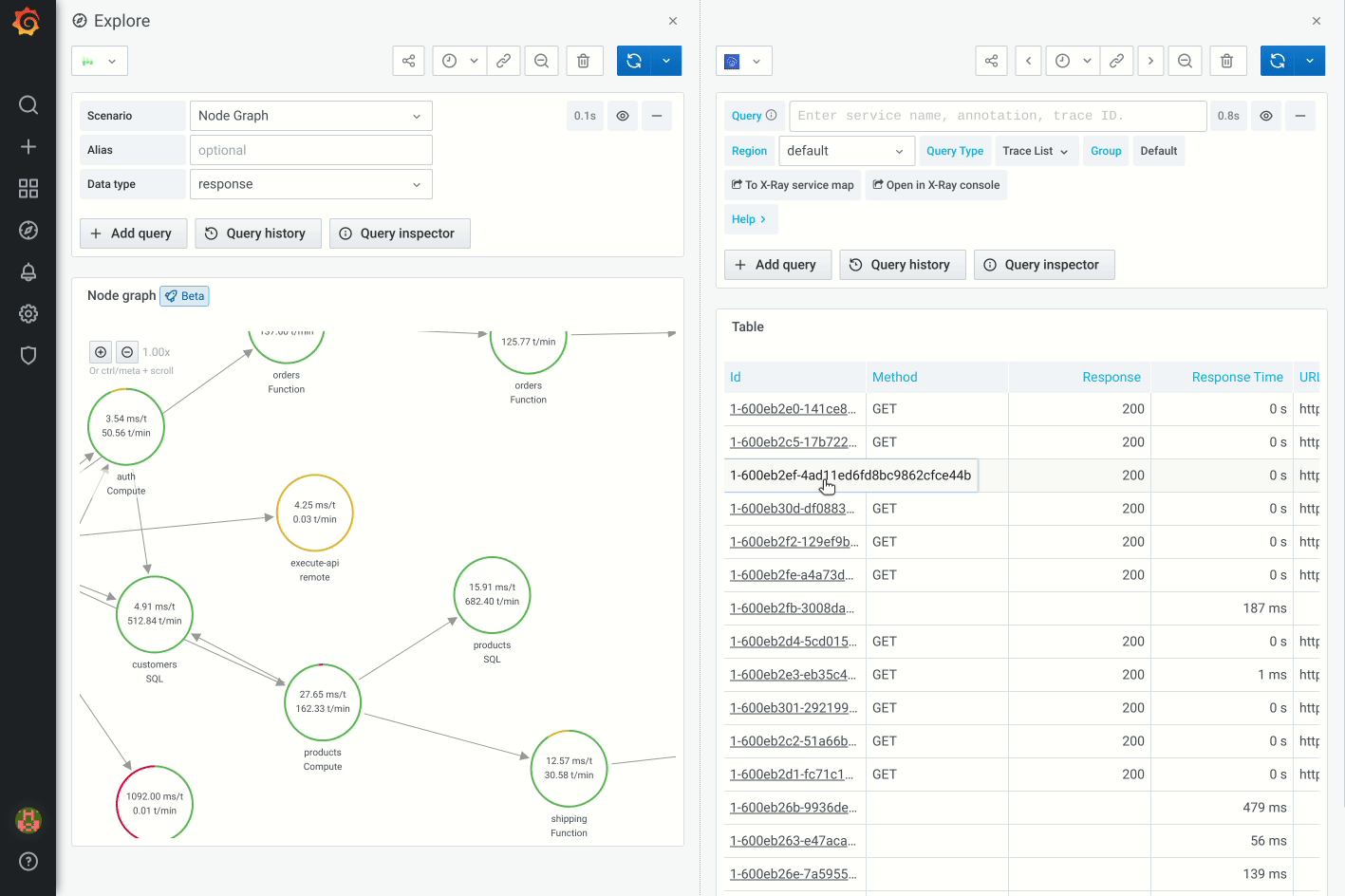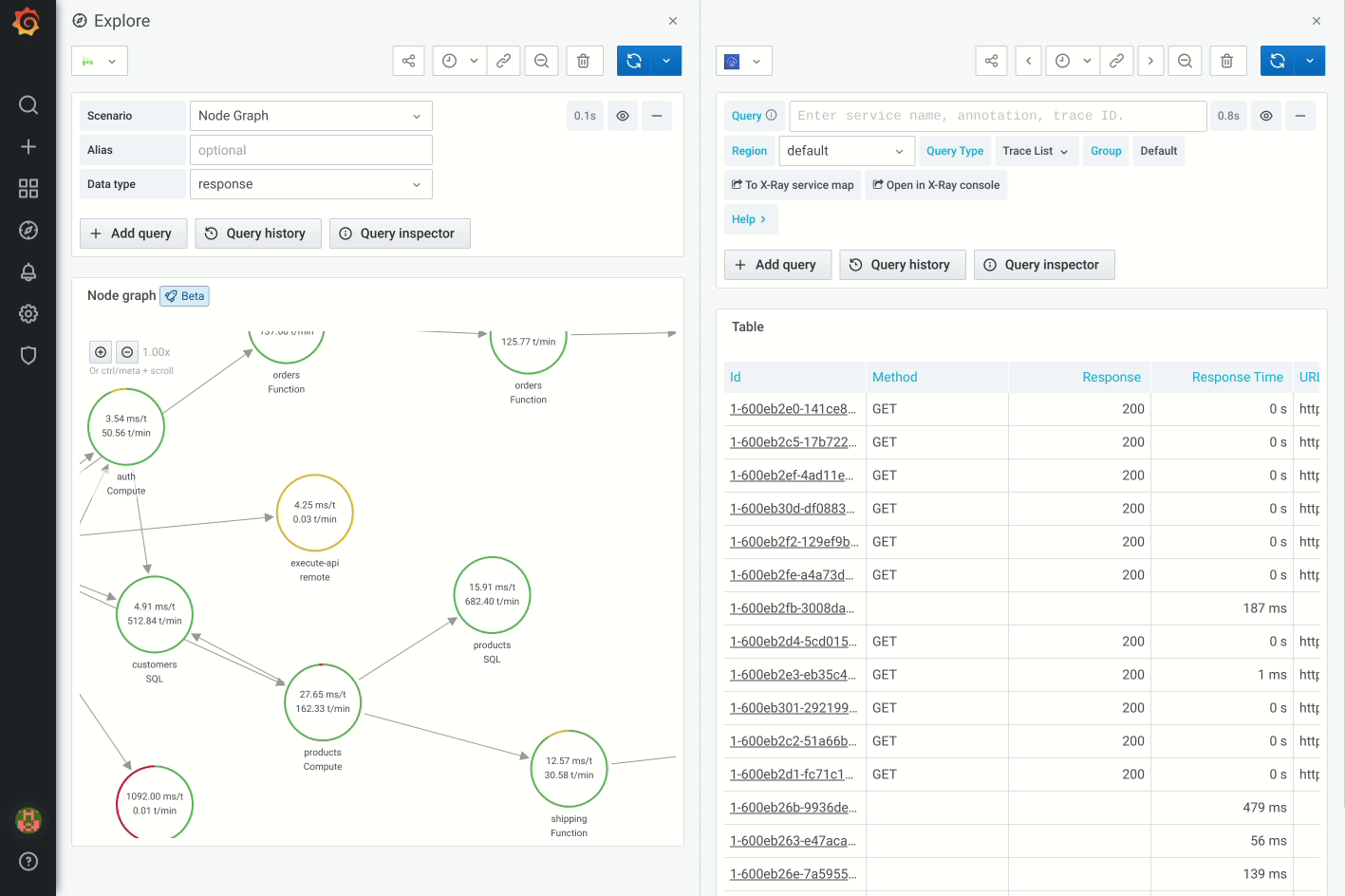
Edges
Edges can also show statistics when you hover over the edge. Similar to nodes, you can open a context menu with additional details and links by clicking on the edge.
The first data source supporting this visualization is X-Ray data source for its Service map feature. For more information, refer to the X-Ray plugin documentation.
Navigating the node graph
You can pan and zoom in or out a node graph.
Zoom in or out
Use the buttons in the upper left corner or use the mouse wheel, touchpad scroll, together with either Ctrl or Cmd key to zoom in or out.
Explore hidden nodes
The number of nodes shown at a given time is limited to maintain a reasonable visualization performance. Nodes that are not currently visible are hidden behind clickable markers that show an approximate number of hidden nodes that are connected by a particular edge. You can click on the marker to expand the graph around that node.
image::node-graph-exploration-8-0.png
Grid view
You can switch to the grid view to have a better overview of the most interesting nodes in the graph. Grid view shows nodes in a grid without edges and can be sorted by stats shown inside the node or by stats represented by the a colored border of the nodes.
image::node-graph-grid-8-0.png
To sort the nodes, click on the stats inside the legend. The marker next to the stat name shows which stat is currently used for sorting and sorting direction.
image::node-graph-legend-8-0.png
Click on the node and select “Show in Graph layout” option to switch back to graph layout and focus on the selected node, to show it in context of the full graph.
image::node-graph-grid-to-default-8-0.png
Data API
This visualization needs a specific shape of the data to be returned from the data source in order to correctly display it.
Node graphs, at minimum, require a data frame describing the edges of the graph. By default, node graphs will compute the nodes and any stats based on this data frame. Optionally a second data frame describing the nodes can be sent in case there is need to show more node specific metadata. You have to set frame.meta.preferredVisualisationType = 'nodeGraph' on both data frames or name them nodes and edges respectively for the node graph to render.
Edges data frame structure
Required fields:
| Field name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
string |
Unique identifier of the edge. |
source |
string |
Id of the source node. |
target |
string |
Id of the target. |
Optional fields:
| Field name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
mainstat |
string/number |
First stat shown in the overlay when hovering over the edge. It can be a string showing the value as is or it can be a number. If it is a number, any unit associated with that field is also shown |
secondarystat |
string/number |
Same as mainStat, but shown right under it. |
detail__* |
string/number |
Any field prefixed with |
thickness |
number |
The thickness of the edge. Default: |
highlighted |
boolean |
Sets whether the edge should be highlighted. Useful, for example, to represent a specific path in the graph by highlighting several nodes and edges. Default: |
Nodes data frame structure
Required fields:
| Field name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
string |
Unique identifier of the node. This ID is referenced by edge in its source and target field. |
Optional fields:
| Field name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
title |
string |
Name of the node visible in just under the node. |
subtitle |
string |
Additional, name, type or other identifier shown under the title. |
mainstat |
string/number |
First stat shown inside the node itself. It can either be a string showing the value as is or a number. If it is a number, any unit associated with that field is also shown. |
secondarystat |
string/number |
Same as mainStat, but shown under it inside the node. |
arc__* |
number |
Any field prefixed with |
detail__* |
string/number |
Any field prefixed with |
color |
string/number |
Can be used to specify a single color instead of using the |
icon |
string |
Name of the icon to show inside the node instead of the default stats. Only Grafana built in icons are allowed (see the available icons here). |
nodeRadius |
number |
Radius value in pixels. Used to manage node size. |
highlighted |
boolean |
Sets whether the node should be highlighted. Useful for example to represent a specific path in the graph by highlighting several nodes and edges. Default: |